This is an implementation of a very compact quantiles sketch with lazy compaction scheme and nearly optimal accuracy per bit of storage. The underlying theoretical work is the paper Optimal Quantile Approximation in Streams, by Zohar Karnin, Kevin Lang, Edo Liberty. The name KLL is composed of the initial letters of the last names of the authors.
This implementation includes 16 variations of the KLL Sketch, including a base KllSketch for methods common to all sketches. The implementation variations are across 3 different dimensions:
With the one exception that the KllItemSketch is not available in direct, updatable form. The classes are organized in an inheritance hierarchy as follows:
The internal package-private variations are constructed using static factory methods from the 4 outer public classes for doubles, floats, items, and longs, respectively
The usage of KllDoublesSketch is very similar to the classic quantiles DoublesSketch.
The starting point for the plot comparisons is setting K in such a way that rank error would be approximately the same. As pointed out above, the default K for both sketches should achieve this. Here is the comparison of the single-sided normalized rank error (getRank() method) for the default K:
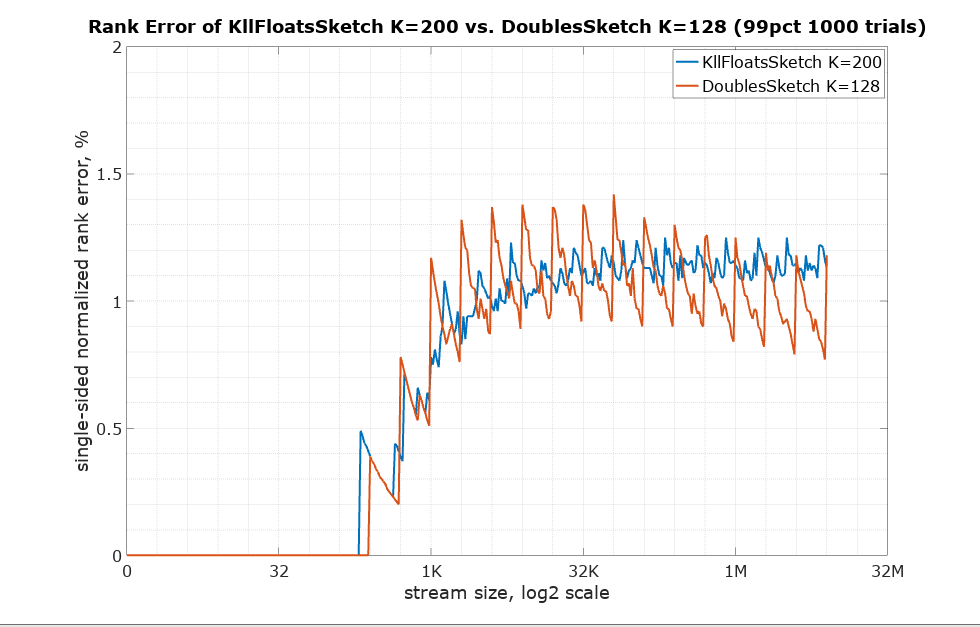
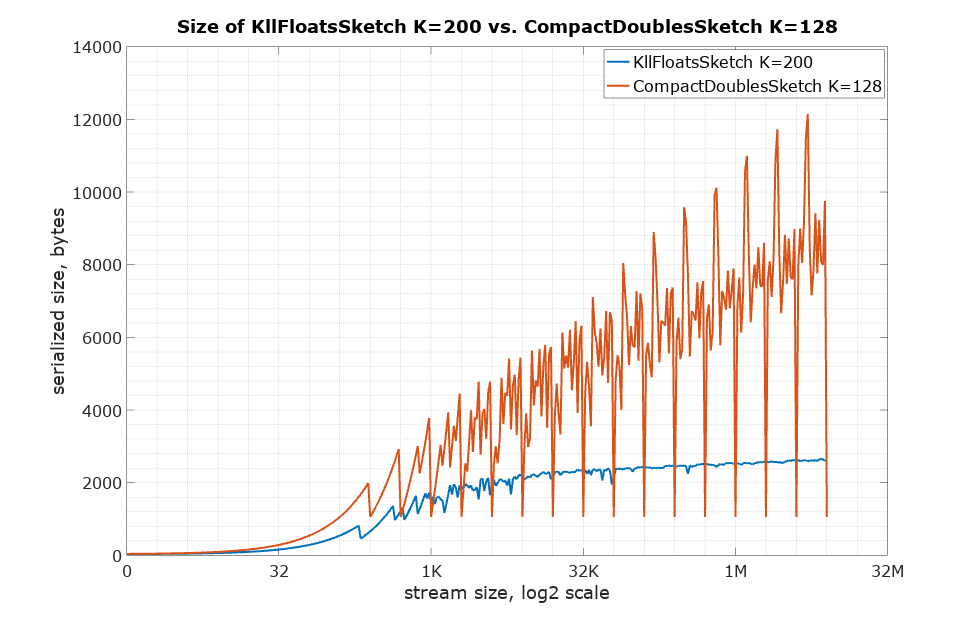
The classic quantiles DoublesSketch has two forms with different serialized sizes: UpdateDoublesSketch and CompactDoublesSketch. The KLL sketches makes this distinction differently. When the KllSketch is serialized using toByteArray() it is always in a compact form and immutable. When the KllSketch is on-heap it is always updatable. It can be created off-heap using the static factory method newDirectInstance(…) method, which is also updatable. It is possible to move from off-heap (Direct) to on-heap using the heapify(Memory) method. The merge(…) method will work with off-heap sketches, on-heap sketches and Memory wrapped compact byte arrays.
Here is the comparison of serialized sizes:
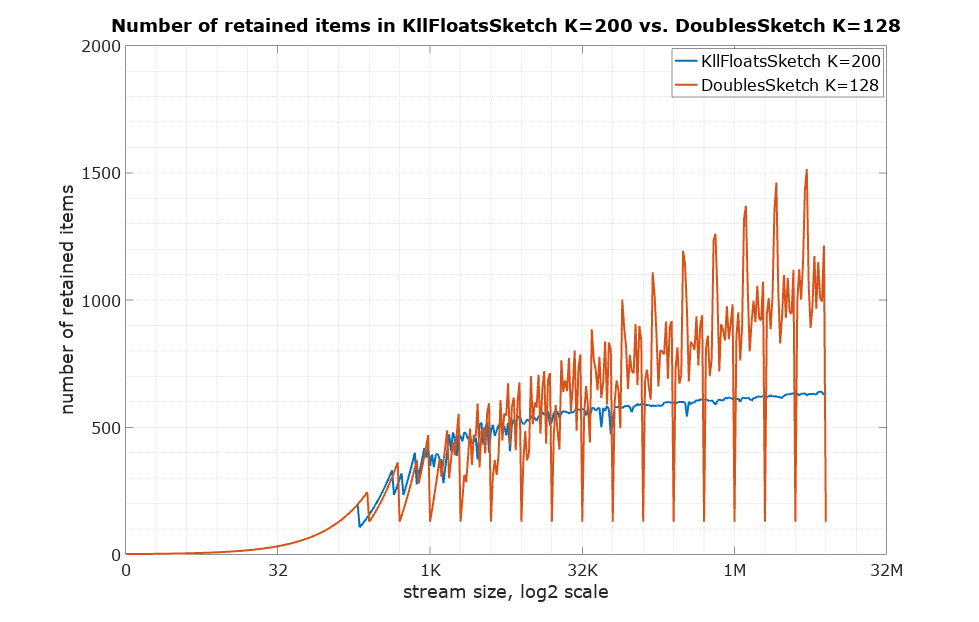
Here is the comparison of the number of retained items to see the difference with no influence of the size of the item type:
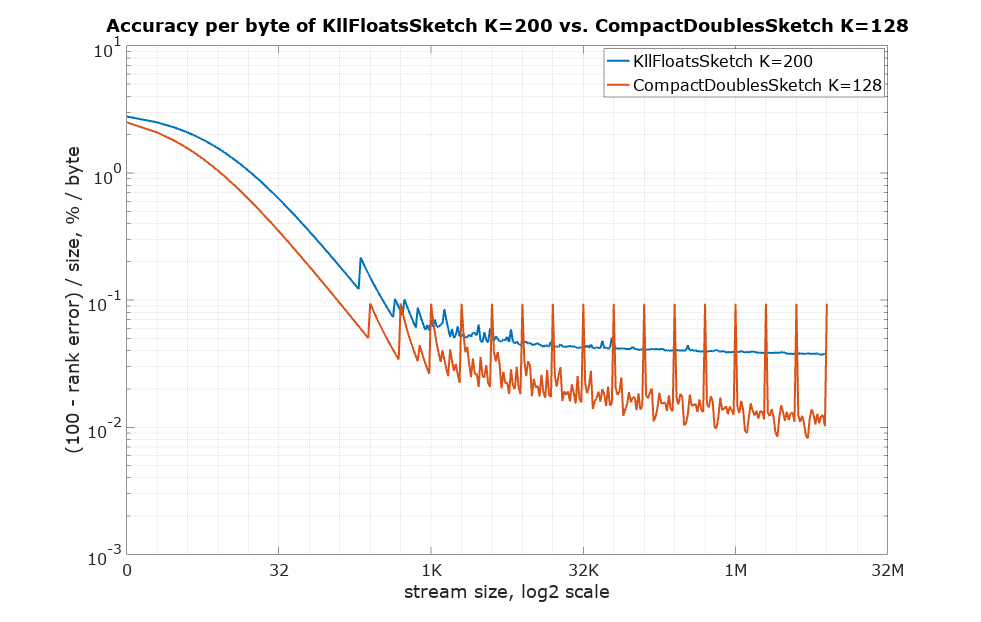
Below is the accuracy per byte measure (the higher the better). Suppose rank error is 1%, so the corresponding accuracy would be 99%. Divide that by size in bytes to arrive at this measure of how expensive each percentage point is in terms of space needed:
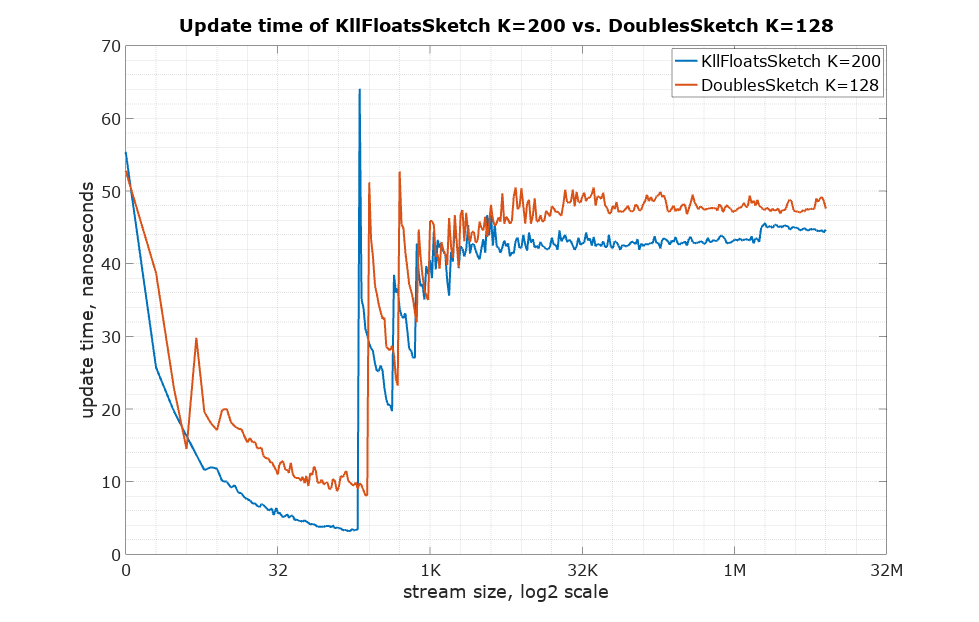
Below is the update() method speed:
import org.apache.datasketches.kll.KllFloatsSketch;
KllFloatsSketch sketch = KllFloatsSketch.newHeapInstance();
int n = 1000000;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sketch.update(i);
}
float median = sketch.getQuantile(0.5);
double rankOf1000 = sketch.getRank(1000);